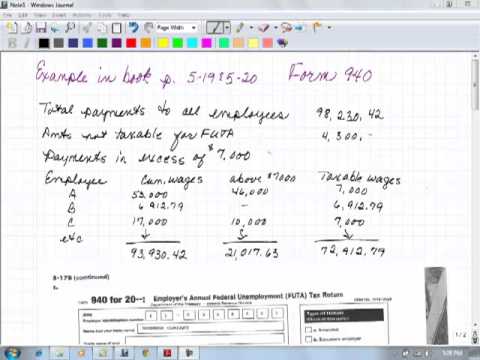
Looking at form 941, examples are given in the book on page 5-19 and 5-20. It is recognized that there is already a payroll register which contains all the necessary information to complete these required payroll forms. By using the information provided in the book, we can understand how the form is put together. If needed, we can do exercises in the book, such as exercise number 95-9. The total payments to all employees are shown on line 3 as $90,823.42. There are certain payments included on line 3 that are not taxable, such as the value of meals and lodging, contributions to employee accident or health plans, employer contributions to retirement plans, and payments to children under 21 for services rendered. This also applies to the value of group term life insurances in excess of $50,000. The $4,300 indicated on page 5-18 is not taxable. Payments exceeding $7,000 are not taxable. For any employee earning $7,001, one dollar is considered in excess of the $7,000 threshold. Examples are provided for employees A, B, and C. Employee A earned $43,053, with $46,000 being taxable. Employee B earned $6,912.79, making their taxable wages zero. Employee C earned $17,000, with $10,000 being above the $7,000 threshold, resulting in taxable wages of $7,000. Examining the examples given in the book, it is evident that employees earning amounts above $7,000 are in the range of $21,762. This indicates that some employees are earning excessively high amounts, while many others are earning significantly less than $7,000. This affects the taxable wages accordingly.
Award-winning PDF software





940 instructions Form: What You Should Know
You may see this form mentioned in your tax return, but you won't pay it. This tax is an equal wage payment that employers, on behalf of their unemployed workers, send to the IRS. When businesses pay the tax each time one of their employees works, they're paying it to the government. For example, if you make 20 an hour, you need to report taxes on your Form 940 each year; if you make 40 an hour, you must make this total at least once a year. You only need to file for tax time if your total wages are 100 or more — your employers reported 100 of your wages on your tax return — and you don't claim other tax credits or deductions. Also, the amount of federal tax withheld from your pay during tax time is used to reduce your employees' taxes paid to the IRS that year. That amounts to part of your employees' federal unemployment tax. Read about tax credits, deductions, and credits. IRS Forms 940, Employer's Estimate of Federal The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FTA), also called the “FTE Tax” by its supporters and “unemployment tax” by its opponents, is a federal tax on wages paid to wage earners. It's an excise tax on a wage that employers have to pay for paying federal income tax, Social Security and Medicaid taxes on their workers' wages paid to the state unemployment insurance system. The federal unemployment tax is usually billed at 40-cents for each 1.00 in wages paid. Employers pay the tax when the first dollar in wages they pay you is taxable. Federal unemployment taxes also apply if your employer pays more than 7.50 per hour (this number is often used interchangeably for the Federal FTE Tax) and withholds more than 200 for federal tax; that is, if your wage rate exceeds 4.25 an hour. In this case, you won't pay the tax until the extra withholding is done. To learn more about the FTE Tax, click here. This page includes an explanation why your wage is classified as “above the poverty level” (GPL) and why the wages of people who make more than one-quarter of the GPL (23,550 for 2017) are also taxed by the state. Also, there are instructions for reporting your FTE tax and paying it.
Online solutions help you to manage your record administration along with raise the efficiency of the workflows. Stick to the fast guide to do Form 940 (Schedule R), steer clear of blunders along with furnish it in a timely manner:
How to complete any Form 940 (Schedule R) online: - On the site with all the document, click on Begin immediately along with complete for the editor.
- Use your indications to submit established track record areas.
- Add your own info and speak to data.
- Make sure that you enter correct details and numbers throughout suitable areas.
- Very carefully confirm the content of the form as well as grammar along with punctuational.
- Navigate to Support area when you have questions or perhaps handle our assistance team.
- Place an electronic digital unique in youR Form 940 (Schedule R) by using Sign Device.
- After the form is fully gone, media Completed.
- Deliver the particular prepared document by way of electronic mail or facsimile, art print it out or perhaps reduce the gadget.
PDF editor permits you to help make changes to youR Form 940 (Schedule R) from the internet connected gadget, personalize it based on your requirements, indicator this in electronic format and also disperse differently.
Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Form 940 instructions